Recession definition: two consecutive quarterly declines in real GDP, but is it that simple?
You might be interested in: 7 FAVORITE WAYS TO BUY A BITCOIN CARD IN 2022
Is a US Recession Around the Corner?
On July 28, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) will release its first estimate of real gross domestic product (GDP) for the second quarter (Q2) of this year. The consensus of the so-called "Blue Chip" companies (companies whose shares are considered a reliable investment) on July 10 is that GDP grew by 1.1 % in the 2nd quarter. However, based on the latest data, S&P Global Market Intelligence estimates that GDP fell by 1.8 % during the quarter. This would follow the 1.6 % Q1 decline already reported by the BEA, thus meeting the aforementioned definition of a recession.
In the US, the official arbiter of recessions is the Business Cycle Dating Committee of the National Economic Research Council. In its meeting, the Committee will consider several other economic indicators in addition to GDP. These include monthly data on industrial production, employment, hours worked and real personal income excluding government welfare payments to households, all of which rose during the first half of the year. So while this situation may turn into a recession, it doesn't look that bright - yet!
However, inflation is unbearably high, unemployment is unsustainably low, and inflation expectations have risen alarmingly above the Federal Reserve's long-term target of 2 %. While recent commodity price pressures will ease, or in some cases reverse, once supply chain bottlenecks are removed, an increase in unemployment will be needed to moderate the lingering inflationary pressures stemming from today's extraordinarily tight labor markets.
The Federal Reserve acknowledged this when, after its June meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee, which sets US monetary policy, it clearly signaled its intention to raise interest rates aggressively. He dropped his previous references that the policy was consistent with strong labor markets.
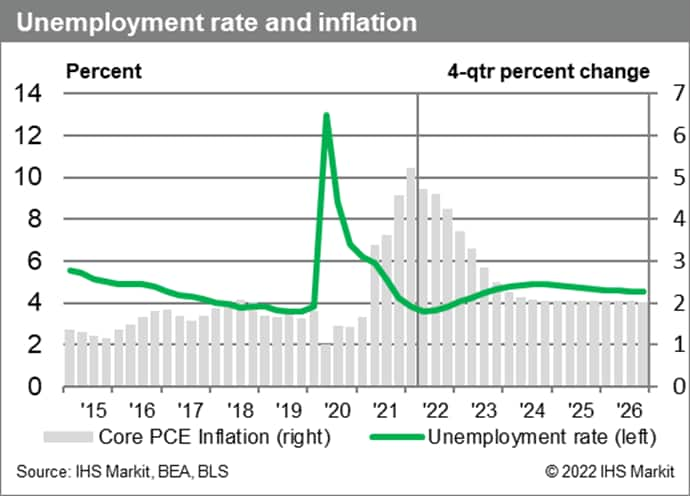
In response, the GDP growth forecast was lowered for 2022 from 2.5 % to 1.4 % and for 2023 from 1.8 % to 1.3 %. As a result, the unemployment rate can be expected to increase by 1.3 percentage points from the current 3.6 % to a peak of 4.9 % by the end of 2024. This period is characterized as a "growth recession" and the subsequent easing of labor market conditions with will prove sufficient to reduce inflation back to 2 %.
However, the historical experience is that since the mid-1960s the unemployment rate has not risen by 1.3 percentage points without rising further, often much more. And that would make the recession…official.
Do not miss: WHERE TO BUY BITCOIN AND CRYPTOMEN











